BMad 方法:核心架構
1. Overview 概覽
The BMad Method is designed to provide agentic modes, tasks and templates to allow repeatable helpful workflows be it for agile agentic development, or expansion into vastly different domains. The core purpose of the project is to provide a structured yet flexible set of prompts, templates, and workflows that users can employ to guide AI agents (like Gemini, Claude, or ChatGPT) to perform complex tasks, guided discussions, or other meaningful domain specific flows in a predictable, high-quality manner.
BMad 方法旨在提供能動模式、任務與範本,以便無論是敏捷能動式開發,或擴展到截然不同的領域,都能實現可重複的有用工作流程。專案的核心目的是提供一組結構化但具彈性的提示、範本與工作流程,使用者可用來引導 AI 代理(如 Gemini、Claude 或 ChatGPT)以可預測且高品質的方式執行複雜任務、引導討論或其他具領域專屬意義的流程。
The systems core module facilitates a full development lifecycle tailored to the challenges of current modern AI Agentic tooling:
系統核心模組促成一個完整的開發生命週期,專為應對當前現代 AI 能動工具的挑戰量身打造:
- Ideation & Planning: Brainstorming, market research, and creating project briefs.
構想與規劃:頭腦風暴、市場調查與建立專案簡報。 - Architecture & Design: Defining system architecture and UI/UX specifications.
架構與設計:定義系統架構與 UI/UX 規格。 - Development Execution: A cyclical workflow where a Scrum Master (SM) agent drafts stories with extremely specific context and a Developer (Dev) agent implements them one at a time. This process works for both new (Greenfield) and existing (Brownfield) projects.
開發執行:一個循環的工作流程,Scrum Master(SM)代理會以極為具體的背景撰寫故事,Developer(Dev)代理則一個接一個地實作它們。此流程適用於新的(Greenfield)以及既有的(Brownfield)專案。
2. 系統架構圖 System Architecture Diagram
The entire BMad-Method ecosystem is designed around the installed bmad-core directory, which acts as the brain of the operation. The tools directory provides the means to process and package this brain for different environments.
整個 BMad-Method 生態系統圍繞已安裝的 bmad-core 目錄設計,該目錄扮演操作的大腦角色。 tools 目錄提供了將這個大腦處理並打包到不同環境的方法。
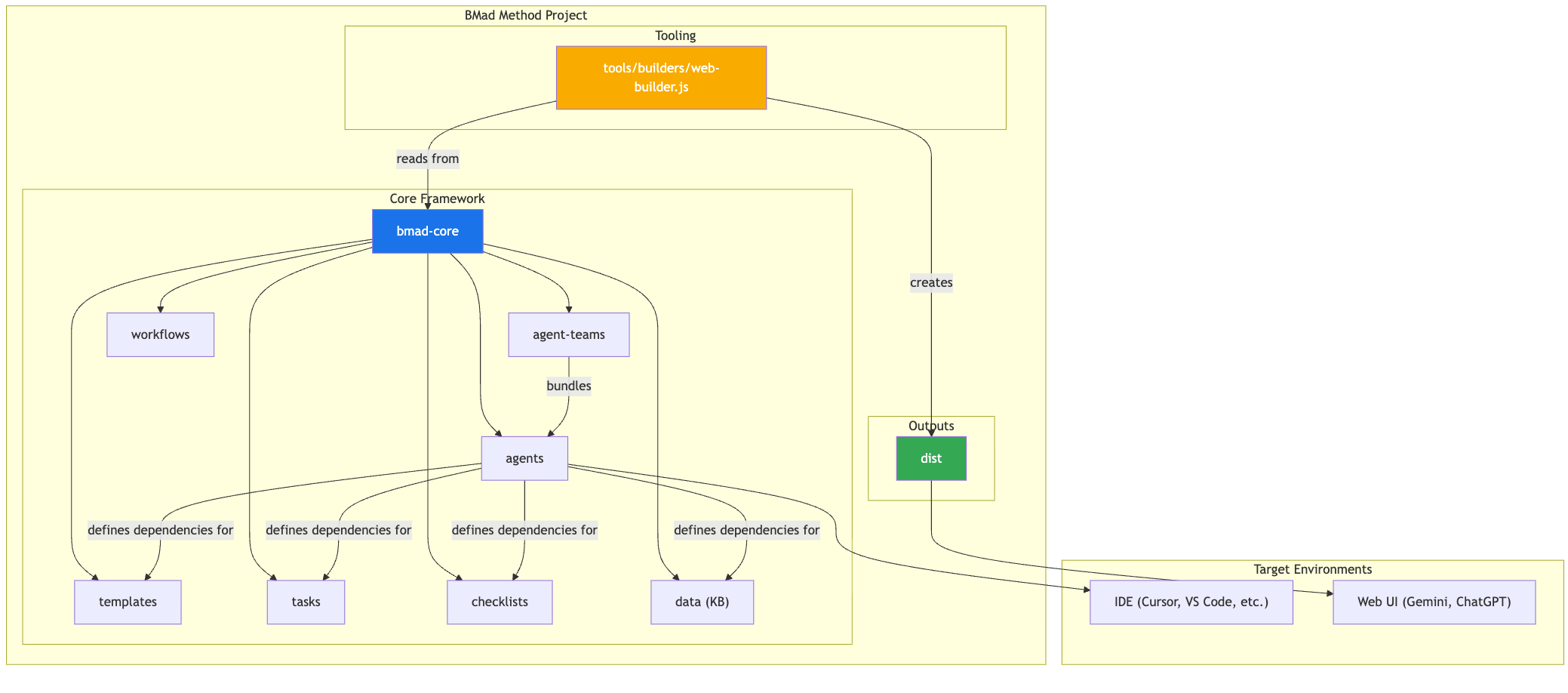
3. Core Components 3. 核心元件
The bmad-core directory contains all the definitions and resources that give the agents their capabilities.bmad-core 目錄包含所有賦予代理人能力的定義與資源。
3.1. Agents 代理人(bmad-core/agents/)
- Purpose: These are the foundational building blocks of the system. Each markdown file (e.g.,
bmad-master.md,pm.md,dev.md) defines the persona, capabilities, and dependencies of a single AI agent.
目的:這些是系統的基礎構建單元。每個 Markdown 檔案(例如bmad-master.md、pm.md、dev.md)定義單一 AI 代理人的角色設定、能力與相依性。 - Structure: An agent file contains a YAML header that specifies its role, persona, dependencies, and startup instructions. These dependencies are lists of tasks, templates, checklists, and data files that the agent is allowed to use.
結構:一個 agent 檔案包含一個 YAML 標頭,指定其角色、人物設定、相依項與啟動指令。這些相依項為代理程式被允許使用的工作清單、範本、檢查表與資料檔案清單。 - Startup Instructions: Agents can include startup sequences that load project-specific documentation from the
docs/folder, such as coding standards, API specifications, or project structure documents. This provides immediate project context upon activation.
啟動指令:代理程式可以包含啟動序列,從docs/資料夾載入專案特定文件,例如程式碼標準、API 規格或專案結構文件。這在啟動時可立即提供專案的上下文。 - Document Integration: Agents can reference and load documents from the project's
docs/folder as part of tasks, workflows, or startup sequences. Users can also drag documents directly into chat interfaces to provide additional context.
文件整合:代理程式可在工作、工作流程或啟動序列中參考並載入專案的docs/資料夾內的文件。使用者也可以直接將文件拖放到聊天介面以提供額外的上下文。 - Example: The
bmad-masteragent lists its dependencies, which tells the build tool which files to include in a web bundle and informs the agent of its own capabilities.
範例:bmad-master代理程式列出其相依項,告訴建置工具在網頁套件中要包含哪些檔案,並告知代理程式其自身的能力。
3.2. Agent Teams (bmad-core/agent-teams/)
- Purpose: Team files (e.g.,
team-all.yaml) define collections of agents and workflows that are bundled together for a specific purpose, like "full-stack development" or "backend-only". This creates a larger, pre-packaged context for web UI environments.
目的:團隊檔案(例如team-all.yaml)定義了為特定目的而打包在一起的代理和工作流程集合,例如「全端開發」或「僅後端」。這為 Web 使用者介面環境建立了更大、預先打包的情境。 - Structure: A team file lists the agents to include. It can use wildcards, such as
"*"to include all agents. This allows for the creation of comprehensive bundles liketeam-all.
結構:團隊檔案列出要包含的代理。它可以使用萬用字元,例如"*"以包含所有代理。這允許建立像team-all這樣的完整套件。
3.3. Workflows (bmad-core/workflows/)
- Purpose: Workflows are YAML files (e.g.,
greenfield-fullstack.yaml) that define a prescribed sequence of steps and agent interactions for a specific project type. They act as a strategic guide for the user and thebmad-orchestratoragent.
目的:工作流程是 YAML 檔案(例如greenfield-fullstack.yaml),用以定義特定專案類型的一連串預定步驟與代理互動。它們作為使用者與bmad-orchestrator代理的策略性指引。 - Structure: A workflow defines sequences for both complex and simple projects, lists the agents involved at each step, the artifacts they create, and the conditions for moving from one step to the next. It often includes a Mermaid diagram for visualization.
結構:工作流程為複雜與簡單專案都定義了步驟序列,列出每個步驟所涉及的代理、他們產生的產物,以及從一個步驟轉換到下一步的條件。它通常包含一個用於視覺化的 Mermaid 圖表。
3.4. 可重用資源 Reusable Resources (templates, tasks, checklists, data)
- Purpose: These folders house the modular components that are dynamically loaded by agents based on their dependencies.
目的:這些資料夾存放模組化元件,代理會根據其相依性動態載入這些元件。templates/: Contains markdown templates for common documents like PRDs, architecture specifications, and user stories.templates/:包含用於常見文件(如 PRD、架構規格和使用者故事)的 Markdown 範本。
tasks/: Defines the instructions for carrying out specific, repeatable actions like "shard-doc" or "create-next-story".tasks/:定義執行特定、可重複操作(如 "shard-doc" 或 "create-next-story")的指示。checklists/: Provides quality assurance checklists for agents like the Product Owner (po) or Architect.checklists/:為像產品負責人(po)或架構師等代理人提供品質保證檢查清單。data/: Contains the core knowledge base (bmad-kb.md), technical preferences (technical-preferences.md), and other key data files.data/:包含核心知識庫(bmad-kb.md)、技術偏好(technical-preferences.md)及其他關鍵資料檔案。
3.4.1. 範本處理系統 Template Processing System
A key architectural principle of BMad is that templates are self-contained and interactive - they embed both the desired document output and the LLM instructions needed to work with users. This means that in many cases, no separate task is needed for document creation, as the template itself contains all the processing logic.
BMad 的一個關鍵架構原則是範本是自包含且具互動性的——它們同時內嵌欲產生的文件輸出與與使用者互動所需的 LLM 指令。這表示在許多情況下,並不需要額外的任務來建立文件,因為範本本身就包含了所有處理邏輯。
The BMad framework employs a sophisticated template processing system orchestrated by three key components:
BMad 框架採用一套由三個關鍵組件協同運作的複雜範本處理系統:
template-format.md(bmad-core/utils/): Defines the foundational markup language used throughout all BMad templates. This specification establishes syntax rules for variable substitution ({{placeholders}}), AI-only processing directives ([[LLM: instructions]]), and conditional logic blocks. Templates follow this format to ensure consistent processing across the system.template-format.md(bmad-core/utils/):定義了整個 BMad 範本中使用的基礎標記語言。本規範建立了變數取代({{placeholders}})、僅 AI 處理指令([[LLM: instructions]])以及條件邏輯區塊的語法規則。範本遵循此格式以確保系統內的一致處理。create-doc.md(bmad-core/tasks/): Acts as the orchestration engine that manages the entire document generation workflow. This task coordinates template selection, manages user interaction modes (incremental vs. rapid generation), enforces template-format processing rules, and handles validation. It serves as the primary interface between users and the template system.create-doc.md(bmad-core/tasks/):擔任協調引擎,管理整個文件生成工作流程。此任務協調範本選擇、管理使用者互動模式(增量式與快速生成)、強制執行範本格式處理規則,並處理驗證。它作為使用者與範本系統之間的主要介面。advanced-elicitation.md(bmad-core/tasks/): Provides an interactive refinement layer that can be embedded within templates through[[LLM: instructions]]blocks. This component offers 10 structured brainstorming actions, section-by-section review capabilities, and iterative improvement workflows to enhance content quality.advanced-elicitation.md(bmad-core/tasks/):提供一個可嵌入於範本中透過[[LLM: instructions]]區塊使用的互動精修層。此元件提供 10 種結構化的頭腦風暴操作、逐節審閱功能以及反覆改進工作流程,以提升內容品質。
The system maintains a clean separation of concerns: template markup is processed internally by AI agents but never exposed to users, while providing sophisticated AI processing capabilities through embedded intelligence within the templates themselves.
系統維持明確的職責分離:樣板標記由內部的 AI 代理處理,但絕不對使用者揭露,同時透過樣板本身內嵌的智慧,提供先進的 AI 處理能力。
3.4.2. 技術偏好系統 Technical Preferences System
BMad includes a personalization layer through the technical-preferences.md file in bmad-core/data/. This file serves as a persistent technical profile that influences agent behavior across all projects.
BMad 在 bmad-core/data/ 的 technical-preferences.md 檔案中加入了個人化層。此檔案作為持久的技術設定檔,會影響所有專案中代理的行為。
Purpose and Benefits: 目的與效益
- Consistency: Ensures all agents reference the same technical preferences
一致性:確保所有代理使用相同的技術偏好設定 - Efficiency: Eliminates the need to repeatedly specify preferred technologies
效率:免去重複指定偏好技術的需要 - Personalization: Agents provide recommendations aligned with user preferences
個人化:代理人提供與使用者偏好一致的建議 - Learning: Captures lessons learned and preferences that evolve over time
學習:擷取隨時間演進的經驗教訓與偏好
Content Structure: The file typically includes preferred technology stacks, design patterns, external services, coding standards, and anti-patterns to avoid. Agents automatically reference this file during planning and development to provide contextually appropriate suggestions.
內容結構:該檔案通常包含偏好的技術棧、設計模式、外部服務、程式碼標準以及應避免的反模式。代理人在規劃與開發時會自動參考此檔案,以提供具情境適切性的建議。
Integration Points: 整合點:
- Templates can reference technical preferences during document generation
範本在文件產生期間可以參考技術偏好 - Agents suggest preferred technologies when appropriate for project requirements
代理人在適合專案需求時會建議偏好的技術 - When preferences don't fit project needs, agents explain alternatives
當偏好不符合專案需求時,代理人會說明替代方案 - Web bundles can include preferences content for consistent behavior across platforms
Web 捆綁包可以包含偏好設定內容,以在各平台上保持一致的行為
Evolution Over Time: Users are encouraged to continuously update this file with discoveries from projects, adding both positive preferences and technologies to avoid, creating a personalized knowledge base that improves agent recommendations over time.
隨著時間演進:鼓勵使用者持續以專案中的發現更新此檔案,新增正面偏好和應避免的技術,建立個人化的知識庫,隨著時間提升代理程式的建議品質。
4. 建置與交付流程 The Build & Delivery Process
The framework is designed for two primary environments: local IDEs and web-based AI chat interfaces. The web-builder.js script is the key to supporting the latter.
該框架針對兩種主要環境設計:本地 IDE 與基於網頁的 AI 聊天介面。 web-builder.js 腳本是支援後者的關鍵。
4.1. 網頁建構器 Web Builder (tools/builders/web-builder.js)
- Purpose: This Node.js script is responsible for creating the
.txtbundles found indist.
目的:此 Node.js 腳本負責建立位於dist的.txt捆綁檔。 - Process: 流程:
- Resolves Dependencies: For a given agent or team, the script reads its definition file.
解決相依性:對於特定的代理或團隊,腳本會讀取其定義檔。
- Resolves Dependencies: For a given agent or team, the script reads its definition file.
- It recursively finds all dependent resources (tasks, templates, etc.) that the agent/team needs.
它會遞迴尋找該代理/團隊所需的所有相依資源(任務、範本等)。 - Bundles Content: It reads the content of all these files and concatenates them into a single, large text file, with clear separators indicating the original file path of each section.
打包內容:它會讀取所有這些檔案的內容,並將它們串接成單一大型文字檔,並以明確的分隔標示每個段落原始的檔案路徑。 - Outputs Bundle: The final
.txtfile is saved in thedistdirectory, ready to be uploaded to a web UI.
輸出包:最終的.txt檔案已儲存在dist目錄,準備上傳到網頁介面。
4.2. 環境特定的使用方式 Environment-Specific Usage
- For IDEs: Users interact with the agents directly via their markdown files in
bmad-core/agents/. The IDE integration (for Cursor, Claude Code, etc.) knows how to call these agents.
對於 IDE:使用者透過位於bmad-core/agents/的 Markdown 檔案直接與代理互動。IDE 整合(例如 Cursor、Claude Code 等)知道如何呼叫這些代理。 - For Web UIs: Users upload a pre-built bundle from
dist. This single file provides the AI with the context of the entire team and all their required tools and knowledge.
對於 Web 使用者介面:使用者上傳來自dist的預先建置套件。這個單一檔案提供 AI 團隊整體的情境,以及所有所需的工具與知識。
5. BMad 工作流程 BMad Workflows
5.1. The Planning Workflow 計畫流程
Before development begins, BMad follows a structured planning workflow that establishes the foundation for successful project execution:
在開始開發之前,BMad 會遵循一套結構化的規劃流程,為專案成功執行建立基礎:
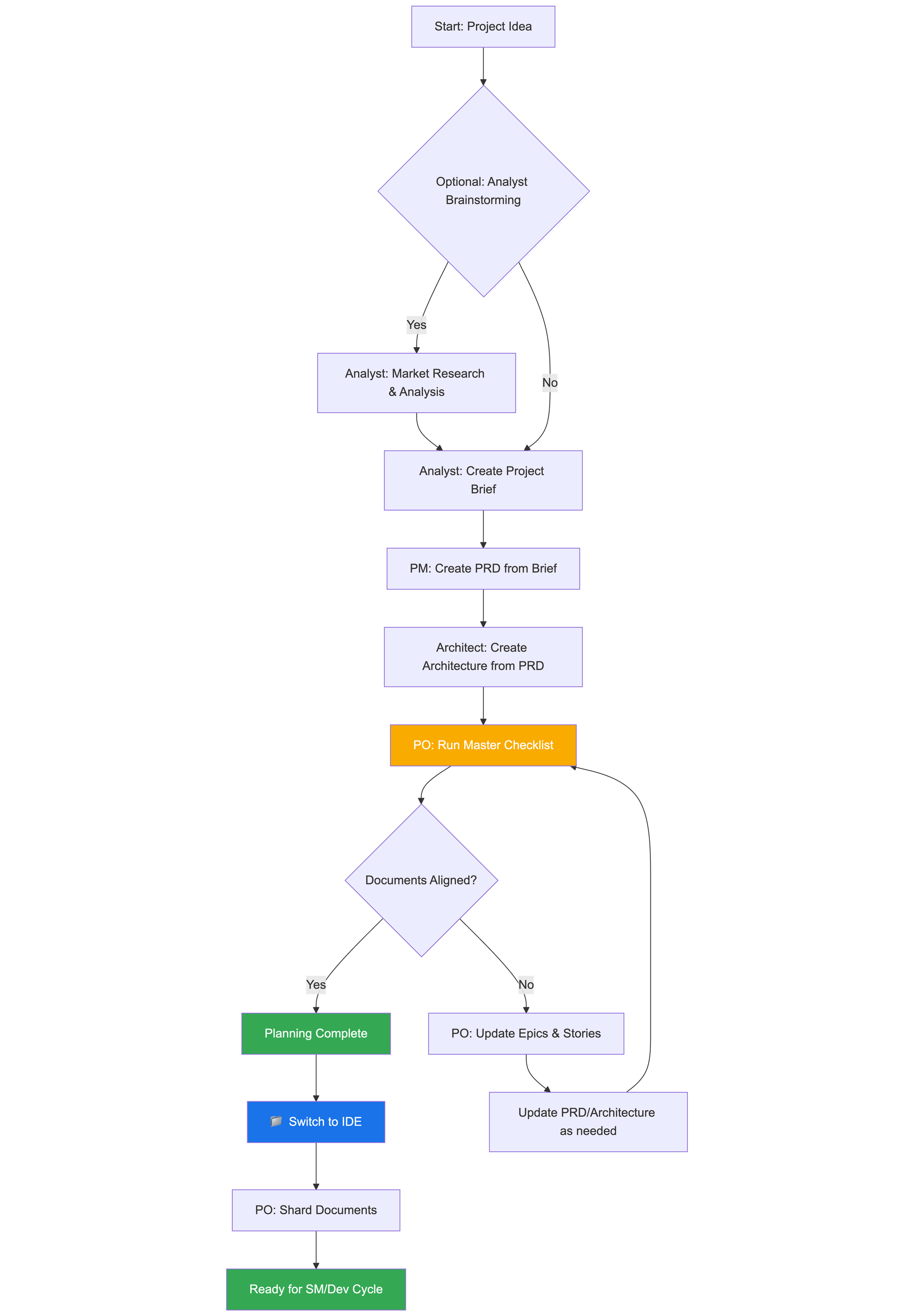
Key Planning Phases: 關鍵規劃階段:
- Optional Analysis: Analyst conducts market research and competitive analysis
可選分析:分析師進行市場研究與競爭對手分析 - Project Brief: Foundation document created by Analyst or user
專案簡報:由分析師或使用者建立的基礎文件 - PRD Creation: PM transforms brief into comprehensive product requirements
產品需求文件建立:產品經理將簡報轉換為完整的產品需求 - Architecture Design: Architect creates technical foundation based on PRD
架構設計:架構師依據產品需求文件建立技術基礎 - Validation & Alignment: PO ensures all documents are consistent and complete
驗證與一致性:產品負責人(PO)確保所有文件的一致性與完整性 - Refinement: Updates to epics, stories, and documents as needed
精煉:根據需要更新大型需求(epics)、使用者故事與文件 - Environment Transition: Critical switch from web UI to IDE for development workflow
環境轉換:開發工作流程從網頁介面切換到整合開發環境(IDE)的關鍵轉變 - Document Preparation: PO shards large documents for development consumption
文件準備:產品負責人將大型文件分割為供開發使用的部分
Workflow Orchestration: The bmad-orchestrator agent uses these workflow definitions to guide users through the complete process, ensuring proper transitions between planning (web UI) and development (IDE) phases.
工作流程編排: bmad-orchestrator 代理使用這些工作流程定義來引導使用者完成整個過程,確保在規劃(Web UI)與開發(IDE)階段之間正確銜接。
5.2. 核心開發週期The Core Development Cycle
Once the initial planning and architecture phases are complete, the project moves into a cyclical development workflow, as detailed in the bmad-kb.md. This ensures a steady, sequential, and quality-controlled implementation process.
一旦初始的規劃與架構階段完成,專案便進入一個循環的開發工作流程,如 bmad-kb.md 中所詳述。這可確保實施過程穩定、循序且具品質管控。
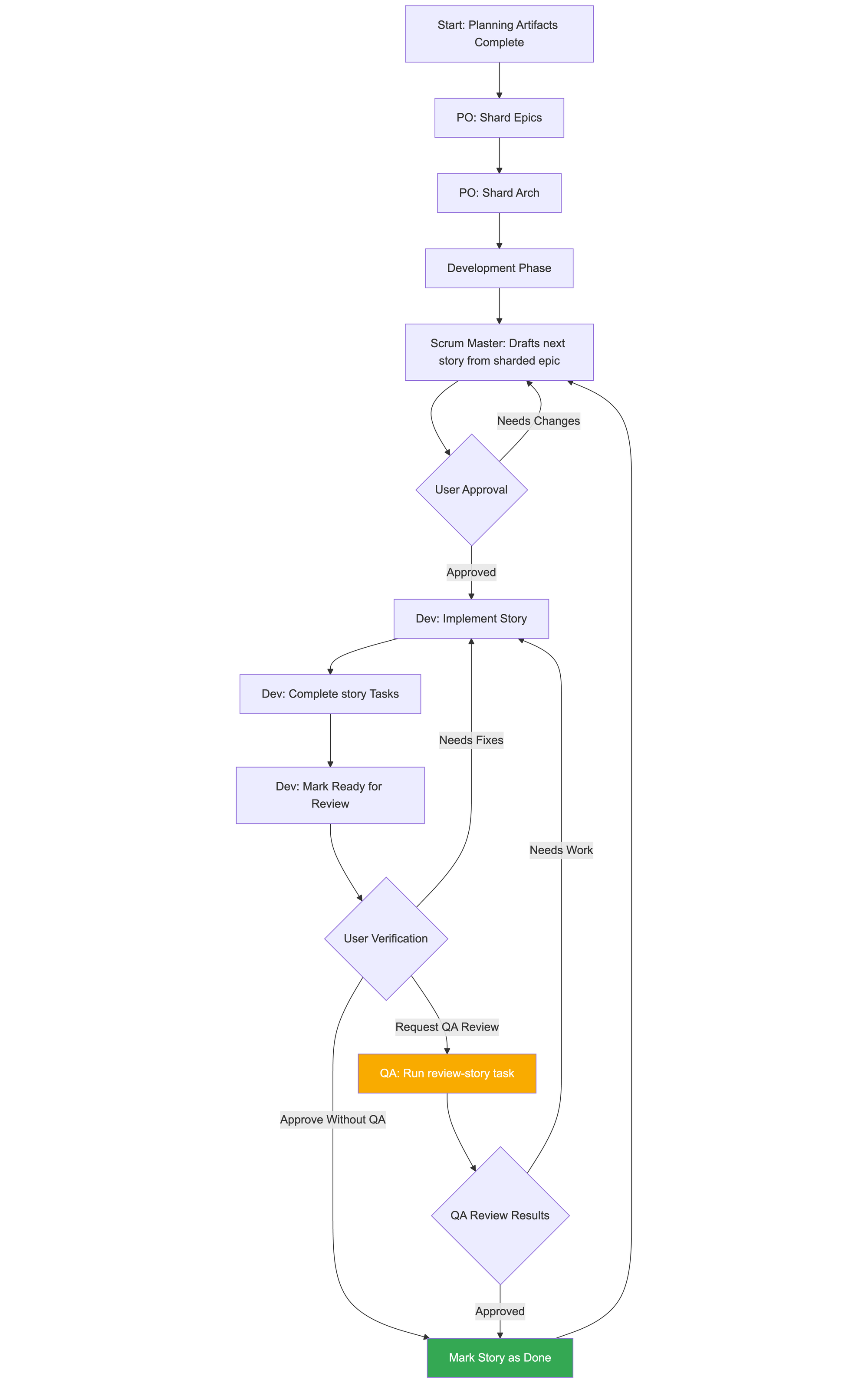
This cycle continues, with the Scrum Master, Developer, and optionally QA agents working together. The QA agent provides senior developer review capabilities through the review-story task, offering code refactoring, quality improvements, and knowledge transfer. This ensures high code quality while maintaining development velocity.
此循環持續進行,由 Scrum Master、開發人員,以及(可選的)QA 代理共同合作。QA 代理透過 review-story 任務提供資深開發人員的審查能力,進行程式碼重構、品質提升與知識傳遞。這確保了高程式碼品質,同時維持開發速度。